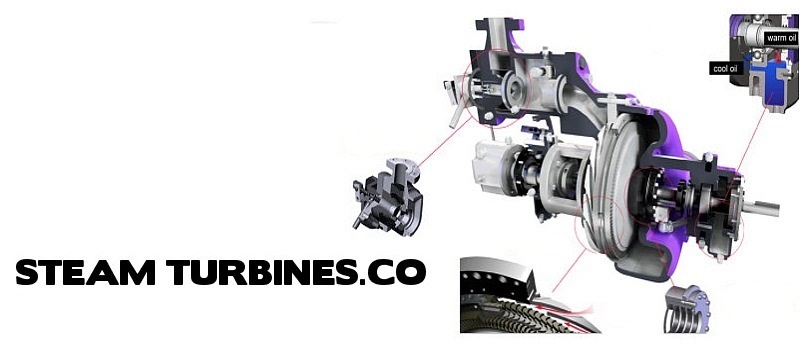
STEAM TURBINE
FAQ
How long has the steam turbine been around?
The modern steam turbine was invented in 1884 by the Charles Parsons, who used it to power a small electrical generator.
What hp range do steam turbines cover?
Steam turbines typically range in size from small 10 hp units used to drives pumps and other rotational equipment, to 1,500,000 kW turbines used to generate electricity.
Our units cover the range of 15 hp to 4800 hp (3.5 MW).
What is the difference between a condensing and non-condensing turbine?
Non-condensing (also called “backpressure” turbines) are most widely used for process steam applications. The exhaust is steam and used in building heating or process heating such as found in pulp and paper mills, food operations or refineries.
[CONT]
Condensing turbines on the other hand exhaust saturated steam (partially condensed state) and this often goes straight to a condenser to turn the steam into condensate for return to the boiler-house.
How is speed regulated in a turbine?
Speed control is carried out with the aid of a governor a device that regulates steam flow to the turbine.
Do the turbines comply with API?
Yes mechanlogy steam turbines are API-611 4th edition compliant.
Why are gearboxes sometimes required with steam turbines?
A steam turbine is most efficient when operating at speeds of 3000 to 6000 rpm while most fans and pumps operate in ranges of 750 to 3600 RPM range. As there is some overlap many times a gearbox is not required.
But often if the speed of the driven unit is lower than 2400 rpm -- especially with larger horsepowers -- a gearbox is used to provide greater efficiency for the turbine.